Please interprete this karyotype and discuss the conditions it can be associated with.
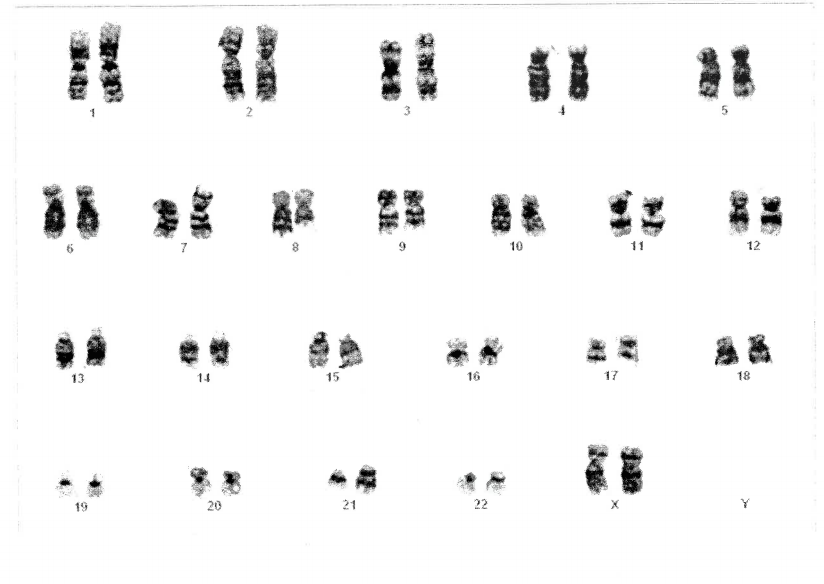
46XX t(8;21)
Translocation of chromosome 8 with chromosome 21 that produces the RUNX1-RUNX1T1 fusion gene. This was previously known as the AML1-ETO gene. The presence of this gene defines Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) irrespective of the percentage of blasts in the bone marrow.
The t(8;21) fuses RUNX1 on chromosome 21 with RUNX1T1 on chromosome 8 to form a RUNX1-RUNX1T1fusion gene. Normal RUNX1 is part of the transcription factor, RUNX1/CBFB which regulates genes that are critical to hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell growth, differentiation and survival. The chimeric RUNX1-RUNX1T1 protein may alter the transcriptional regulation of normal RUNX1/CBFB target genes and activate new target genes.
The presence of the t(8;21) in adults confers a good prognosis. It is seen in 1-8% of adults with AML. It classifies the leukemia into the good prognostic category by European Leukemia Network (ELN) classification. This leukaemia, like other core binding factor leukemias are often responsive to cytarabine based treatment. Standard treatment does not include consideration of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation.
The t(8;21) in children however, whilst it is the most common translocation present in AML, confers a poor prognosis.